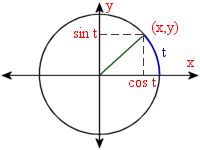
Since I noticed I had to keep looking some of these up, I place them here, just for reference, gathered from around the internet. Many of these formulas can be written in different ways, but I have simplified them as much as possible.
Where, \(\phi=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}=1.6180339887498948482045868\ldots\), also known as the golden ratio (phi).
| a | sin(a) = cos(b) = sin(90-b) = cos(90-a) | tan(a) = cot(b) = tan(90-b) = cot(90-a) | b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| deg | rad | deg | rad | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90 | π/2 |
| 3 | π/60 | \(\frac{1}{16}\left[(2-2\sqrt3)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5}+\sqrt2(-1+\sqrt{5})(1+\sqrt3)\right]\) | \(\frac14\left[(2-\sqrt{3})(3+\sqrt{5})-2\right]\left[2-\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}\right]\) | 87 | 29π/30 |
| 6 | π/30 | \(\frac{1}{8} \left[\sqrt{30-6\sqrt5}-\sqrt5-1\right]\) | \(\frac12\left[\sqrt{10-2\sqrt5}-\sqrt3(-1+\sqrt5)\right]\) | 84 | 7π/15 |
| 9 | π/20 | \(\frac12\sqrt{2-\sqrt{2+\phi}}=\frac12\sqrt{2-\sqrt{\frac{5+\sqrt5}{2}}}\) | \(1+\sqrt5-\sqrt{5+2\sqrt5}\) | 81 | 9π/20 |
| 12 | π/15 | \(\frac{1}{8}\left[\sqrt{10+2\sqrt5}-\sqrt3(-1+\sqrt5)\right]\) | \(\frac12\left[\sqrt3(3-\sqrt5)-\sqrt{2(25-11\sqrt5)}\right]\) | 78 | 13π/30 |
| 15 | π/12 | \(\frac{\sqrt{6}-\sqrt{2}}{4} =\frac{\sqrt{2-\sqrt{3}}}{2}\) | \(2-\sqrt{3}\) | 75 | 5π/12 |
| 18 | π/10 | \(\frac{1}{2\phi}=\frac{1}{1+\sqrt{5}}=\frac{\sqrt{5}-1}{4}\) | \(\frac15\sqrt{25-10\sqrt5}\) | 72 | 2π/5 |
| 21 | 7π/60 | \(\frac{1}{16}\left[2(\sqrt3+1)\sqrt{5-\sqrt5}-\sqrt2(\sqrt3-1)(1+\sqrt5)\right]\) | \(\frac{1}{4}\left[2-(2+\sqrt3)(3-\sqrt5)\right]\left[2-\sqrt{2(5+\sqrt5)}\right]\) | 69 | 23π/60 |
| 22.5 | π/8 | \(\frac{1}{2} \sqrt{2 – \sqrt{2}}\) | \(\sqrt{2} – 1\) | 67.5 | 3π/8 |
| 24 | 2π/15 | \(\frac{1}{8}\left[-\sqrt{10-2\sqrt5}+\sqrt3(1+\sqrt5)\right]\) | \(\frac12\left[-\sqrt3(3+\sqrt5)+\sqrt{2(25+11\sqrt5)}\right]\) | 66 | 11π/30 |
| 27 | 3π/20 | \(\frac12\sqrt{2-\sqrt{2-\frac{1}{\phi}}}=\frac12\sqrt{2-\sqrt{\frac{5-\sqrt5}{2}}}\) | \(-1+\sqrt5-\sqrt{5-2\sqrt5}\) | 63 | 7π/20 |
| 30 | π/6 | \(\frac12\) | \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) | 60 | π/3 |
| 33 | 11π/60 | \(\frac{1}{16}\left[2(\sqrt3-1)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5}+\sqrt2(1+\sqrt3)(\sqrt5-1)\right]\) | \(\frac{1}{4}\left[2-(2-\sqrt3)(3+\sqrt5)\right]\left[2+\sqrt{2(5-\sqrt5)}\right]\) | 57 | 19π/60 |
| 36 | π/5 | \(\frac12\sqrt{3-\phi}=\sqrt{\frac{5-\sqrt5}{8}}\) | \(\sqrt{5-2\sqrt5}\) | 54 | 3π/10 |
| 39 | 13π/60 | \(\frac1{16}[2(1-\sqrt3)\sqrt{5-\sqrt5}+\sqrt2(\sqrt3+1)(\sqrt5+1)]\) | \(\frac14\left[(2-\sqrt3)(3-\sqrt5)-2\right]\left[2-\sqrt{2(5+\sqrt5)}\right]\) | 51 | 17π/60 |
| 42 | 7π/30 | \(\frac{1}{8} \left[\sqrt{30+6\sqrt5}-\sqrt5+1\right]\) | \(\frac12\left[-\sqrt{10+2\sqrt5}+\sqrt3(1+\sqrt5)\right]\) | 48 | 4π/15 |
| 45 | π/4 | \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) | 1 | 45 | π/4 |
| 48 | 4π/15 | \(\frac{1}{8}\left[\sqrt{10+2\sqrt5}+\sqrt3(-1+\sqrt5)\right]\) | \(\frac12\left[\sqrt3(3-\sqrt5)+\sqrt{2(25-11\sqrt5)}\right]\) | 42 | 7π/30 |
| 51 | 17π/60 | \(\frac1{16}[2(1+\sqrt3)\sqrt{5-\sqrt5}+\sqrt2(\sqrt3-1)(\sqrt5+1)]\) | \(\frac14\left[(2+\sqrt3)(3-\sqrt5)-2\right]\left[2+\sqrt{10+2\sqrt5}\right]\) | 39 | 13π/60 |
| 54 | 3π/10 | \(\frac{\phi}{2}=\frac{1+\sqrt5}{4}\) | \(\frac15\sqrt{25+10\sqrt5}\) | 36 | π/5 |
| 57 | 19π/60 | \(\frac{1}{16}\left[2(\sqrt3+1)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5}+\sqrt2(1-\sqrt3)(\sqrt5-1)\right]\) | \(\frac{1}{4}\left[2-(2+\sqrt3)(3+\sqrt5)\right]\left[2-\sqrt{2(5-\sqrt5)}\right]\) | 33 | 11π/60 |
| 60 | π/3 | \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) | \(\sqrt{3}\) | 30 | π/6 |
| 63 | 7π/20 | \(\frac12 \sqrt{2+\sqrt{2-\frac{1}{\phi}}}=\frac12\sqrt{2+\sqrt{\frac{5-\sqrt5}{2}}}\) | \(-1+\sqrt5+\sqrt{5-2\sqrt5}\) | 27 | 3π/20 |
| 66 | 11π/30 | \(\frac{1}{8} \left[\sqrt{30-6\sqrt5}+\sqrt5+1\right]\) | \(\frac12\left[\sqrt{10-2\sqrt5}+\sqrt3(-1+\sqrt5)\right]\) | 24 | 2π/15 |
| 67.5 | 3π/8 | \(\frac{1}{2} \sqrt{2 + \sqrt{2}}\) | \(\sqrt{2} + 1\) | 22.5 | π/8 |
| 69 | 23π/60 | \(\frac{1}{16}\left[2(\sqrt3-1)\sqrt{5-\sqrt5}+\sqrt2(\sqrt3+1)(1+\sqrt5)\right]\) | \(\frac{1}{4}\left[2-(2-\sqrt3)(3-\sqrt5)\right]\left[2+\sqrt{2(5+\sqrt5)}\right]\) | 21 | 7π/60 |
| 72 | 2π/5 | \(\frac{\sqrt{2+\phi}}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{5+\sqrt5}}{2\sqrt2}\) | \(\sqrt{5+2\sqrt5}\) | 18 | π/10 |
| 75 | 5π/12 | \(\frac{\sqrt{2+\sqrt{3}}}{2}\) | \(2+\sqrt{3}\) | 15 | π/12 |
| 78 | 13π/30 | \(\frac{1}{8} \left[\sqrt{30+6\sqrt5}+\sqrt5-1\right]\) | \(\frac12\left[\sqrt{10+2\sqrt5}+\sqrt3(1+\sqrt5)\right]\) | 12 | π/15 |
| 81 | 9π/20 | \(\frac12\sqrt{2+\sqrt{2+\phi}}=\frac12\sqrt{2+\sqrt{\frac{5+\sqrt5}{2}}}\) | \(1+\sqrt5+\sqrt{5+2\sqrt5}\) | 9 | π/20 |
| 84 | 7π/15 | \(\frac{1}{8} \left[\sqrt{10-2\sqrt5}+\sqrt3(1+\sqrt5)\right]\) | \(\frac12\left[\sqrt3(3+\sqrt5)+\sqrt{2(25+11\sqrt5)}\right]\) | 6 | π/30 |
| 87 | 29π/30 | \(\frac{1}{16}\left[(2+2\sqrt{3})\sqrt{5+\sqrt{5}}+\sqrt{2}(-1+\sqrt{5})(-1+\sqrt{3})\right]\) | \(\frac14\left[(2+\sqrt{3})(3+\sqrt{5})-2\right]\left[2+\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}\right]\) | 3 | π/60 |
| 90 | π/2 | 1 | \(\infty\) | 0 | 0 |
| deg | rad | sin(a) = cos(b) = sin(90-b) = cos(90-a) | tan(a) = cot(b) = tan(90-b) = cot(90-a) | deg | rad |
| a | b | ||||
\begin{array}{r|l|l|l}
rad
& deg
& \sin
& \cos
& \tan
\\
\hline 2\pi
& 360
& 0
& 1
& 0
\\
\hline \pi
& 180
& 0
& -1
& 0
\\
\hline \frac{2\pi}{3}
& 120
& \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{3}
& -\frac{1}{2}
& -\sqrt{3}
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{2}
& 90
& 1
& 0
& \pm\infty
\\
\hline \frac{2\pi}{5}
& 72
& \frac{1}{4}\left(\sqrt{10+2\sqrt{5}}\right)
& \frac{1}{4}\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)
& \sqrt{5+2\sqrt{5}}
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{3}
&60
& \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{3}
& \frac{1}{2}
& \sqrt{3}
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{4}
&45
& \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{2}
& \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{2}
& 1
\\
\hline \frac{2\pi}{9}
& 40
& \frac{i}{2}\left(\sqrt[3]{\frac{-1-\sqrt{-3}}{2}}-\sqrt[3]{\frac{-1+\sqrt{-3}}{2}}\right)
& \frac{1}{2}\left(\sqrt[3]{\frac{-1+\sqrt{-3}}{2}}+\sqrt[3]{\frac{-1-\sqrt{-3}}{2}}\right)
&
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{5}
& 36
& \frac{1}{4}\left(\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}\right)
& \frac{1}{4}\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)
& \sqrt{5-2\sqrt{5}}
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{6}
& 30
& \frac{1}{2}
& \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{3}
& \frac{1}{3}\sqrt{3}
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{7}
&
& \frac{1}{24}\sqrt{3\left(112-\sqrt[3]{14336+\sqrt{-5549064193}}-\sqrt[3]{14336-\sqrt{-5549064193}}\right)}
& \frac{1}{24}\sqrt{3\left(80+\sqrt[3]{14336+\sqrt{-5549064193}}+\sqrt[3]{14336-\sqrt{-5549064193}}\right)}
&
\\
\hline \frac{2\pi}{15}
& 24
& \frac{1}{8}\left(\sqrt{15}+\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}\right)
& \frac{1}{8}\left(1+\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{30-6\sqrt{5}}\right)
& \frac{1}{2}\left(-3\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{15}+\sqrt{50+22\sqrt{5}}\right)
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{8}
& 22.5
& \frac{1}{2}\left(\sqrt{2-\sqrt{2}}\right)
& \frac{1}{2}\left(\sqrt{2+\sqrt{2}}\right)
& \sqrt{2}-1
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{9}
& 20
& \frac{i}{4}\left(\sqrt[3]{4-4\sqrt{-3}}-\sqrt[3]{4+4\sqrt{-3}}\right)
& \frac{1}{4}\left(\sqrt[3]{4+4\sqrt{-3}}+\sqrt[3]{4-4\sqrt{-3}}\right)
&
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{10}
& 18
& \frac{1}{4}\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)
& \frac{1}{4}\left(\sqrt{10+2\sqrt{5}}\right)
& \frac{1}{5}\left(\sqrt{25-10\sqrt{5}}\right)
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{12}
& 15
& \frac{1}{4}\left(\sqrt{6}-\sqrt{2}\right)
& \frac{1}{4}\left(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}\right)
& 2-\sqrt{3}
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{15}
& 12
& \frac{1}{8}\left[\sqrt{10+2\sqrt5}-\sqrt3(-1+\sqrt5)\right]
& \frac{1}{8} \left[\sqrt{30+6\sqrt5}+\sqrt5-1\right]
&
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{18}
&10
&
&
&
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{30}
& 6
& \frac{1}{8} \left[\sqrt{30-6\sqrt5}-\sqrt5-1\right]
& \frac{1}{8} \left[\sqrt{10-2\sqrt5}+\sqrt3(1+\sqrt5)\right]
&
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{40}
& 4.5
& \frac{1}{2} \sqrt{2-\sqrt{2+\sqrt{\frac{5+\sqrt{5}}{2}}}}
& \frac{1}{2} \sqrt{2+\sqrt{2+\sqrt{\frac{5+\sqrt{5}}{2}}}}
&
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{45}
& 4
&
&
&
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{60}
&3
& \frac{1}{16}\left[(2-2\sqrt3)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5}+\sqrt2(-1+\sqrt{5})(1+\sqrt3)\right]
& \frac{1}{16}\left[(2+2\sqrt{3})\sqrt{5+\sqrt{5}}+\sqrt{2}(-1+\sqrt{5})(-1+\sqrt{3})\right]
&
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{90}
&2
&
&
&
\\
\hline \frac{\pi}{180}
&1
& \frac1{2i}\left[\sqrt[3]{\cos(3^\circ) + i\sin(3^\circ)} – \sqrt[3]{cos(3^\circ) – i\sin(3^\circ)} \right]
&
&
\end{array}
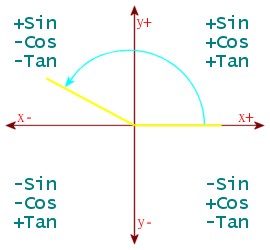
The values for angles outside the range 0-90 degrees, can be found by reducing the angle be in the correct range. Negative angles should have 360 added to them until positive. If angle ≥360, subtract multiples of 360 from it, until <360. Then, if angle ≥270, subtract from 360. If angle ≥180, subtract 180. If angle ≥90, subtract from 180.
Examples:
- sin(-54)=sin(360-54)=sin(306)=-sin(54)
- cos(120)=cos(180-120)=-cos(60)
- tan(225)=tan(225-180)=tan(45)
- tan(-225)=tan(360-225)=tan(135)=tan(180-135)=-tan(45)
- sin(1000)=sin(1000-360*2)=sin(280)=sin(360-280)=-sin(80)
Angles between 0 and 360 will have the following signs and are measured in a counter-clockwise arc originating at the “x+” line.
FYI, here is the exact value of sin 1°, \( \frac1{2i}\left[\sqrt[3]{\cos(3) + i\sin(3)} – \sqrt[3]{cos(3) – i\sin(3)} \right] \), where \(i=\sqrt{-1}\),
\( \frac12(-1-i\sqrt3)\sqrt[3]{-\frac{\sqrt6}{384} (\sqrt5-1)(3+\sqrt3)+ \frac{\sqrt3}{192}(3-\sqrt3)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5}+\frac{i}{8}\sqrt{1-\frac1{48}\left[\sqrt6(\sqrt5-1)(3+\sqrt3)-2\sqrt3(3-\sqrt3)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5} \right]^2} } +
\\ \frac12(-1+i\sqrt3)\sqrt[3]{-\frac{\sqrt6}{384} (\sqrt5-1)(3+\sqrt3)+ \frac{\sqrt3}{192}(3-\sqrt3)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5}-\frac{i}{8}\sqrt{1-\frac1{48}\left(\sqrt6(\sqrt5-1)(3+\sqrt3)-2\sqrt3(3-\sqrt3)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5} \right)^2} } \)
and the cos 1°,
\(\frac12\sqrt{2-
(i\sqrt3-1)\sqrt[3]{\frac{-\sqrt3}{64}(1+\sqrt5)-\frac{\sqrt2}{128}(\sqrt5-1)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5} + \frac{i}{8}\sqrt{1-\left[\frac{\sqrt3}{8}(1+\sqrt5)+\frac{\sqrt2}{16}(\sqrt5-1)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5}\right]^2}} +
\\(i\sqrt3+1)\sqrt[3]{\frac{-\sqrt3}{64}(1+\sqrt5)-\frac{\sqrt2}{128}(\sqrt5-1)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5} – \frac{i}{8}\sqrt{1-\left[\frac{\sqrt3}{8}(1+\sqrt5)+\frac{\sqrt2}{16}(\sqrt5-1)\sqrt{5+\sqrt5}\right]^2}}
}\)